Locking Electronics: FALC & PFD
簡単操作の位相周波数ロッキング
- 堅牢な位相および周波数ロッキング
- 完全なリモート制御が可能
- DFC GUI (TOPAS DFC)に組み込まれた便利なソフトウェア機能
- オフセット位相周波数ロックのための可変RFソース
- 10 MHz リファレンス入力
- ビート検出 & 周波数カウントのための信号最適化機能
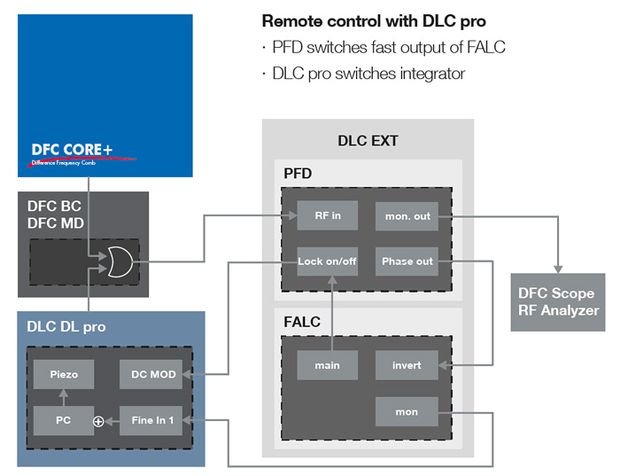
位相周波数検出器(PFD)とFALC 110から構成されたDFCロッキングエレクトロニクスは光周波数コムアプリケーションに対して優れた位相周波数ロッキング機能を提供します。PFDのRF信号入力はDFC MDのRF出力信号で使用するように設計されています。PFDによって生成されたエラー信号はFALC 110レギュレータの入力用に供給されます。 FALCのメイン出力はPFDを通過して半導体レーザー電流を変調する高速フィードバック回路のリモートスイッチングを可能にします。エラー信号のコピー(mon.out)はDL pro半導体レーザー走査用ピエゾ素子 (Fine In) とDLC pro半導体レーザーコントローラの全てのデジタルPID上でスローなフィードバックループ閉回路を構成するために使用されます。DFC UIソフトウェア(TOPAS DFC)上のボタン操作により低速および高速のフィードバックループを有効または無効にすることができます。
例:DLC DL proからDFCへの位相周波数ロック (ビデオを見る)
Request a Quotation Download the Product Brochure Application Note Phase and Frequency Locking of Diode Lasers
-
Specification
PFD FALC110 DLC pro Lock DFC CORE +
internal LockDescription Phase Frequency Detector Fast Analog PID All-digital PID All-digital PID Recommended for lock of DL pro to DFC x x x Recommended for lock of DFC
to opt. referencex x x Task Error signal generation High bandwidth phase lock Slow feedback to DLC pro laser Slow feedback to DFC Max. bandwidth ≈ 45 MHz ≈ 30 kHz ≈ 30 kHz Remote control x via PFD x x Rack compatibility x x x x Stand alone x optional software license for DLC pro included in any DFC CORE + Power supply DLC Ext DLC Ext Dimensions PFD, FALC110, DLC EXT 131 x 184 x 286 mm³ included in DLC pro included in DFC CORE + -
Applications
The DFC locking electronics consisting of the Phase Frequency Detector (PFD) and FALC 110 provides high-end phase frequency locking for comb applications. The PFD RF input is designed for use with the RF output signal of the DFC MD. The error signal generated by the PFD is fed to the input of the FALC 110 regulator. The main output of the FALC is passed through the PFD to allow for remote switching of the fast feedback loop which modulates the laser diode current. A copy of the error signal (mon. out) is used to close the slow feedback loop acting on the DL pro piezo (Fine In) with the all-digital PID of the DLC pro. Slow and fast feedback loop can be enabled and disabled with a push of a button in the DFC user interface (TOPAS DFC).
-
Downloads
- Product Brochure: Optical Clocks
- Product Brochure: Rydberg Flyer
-
Literature
- Scientific Article: E. Benkler et al., End-to-end topology for fiber comb based optical frequency transfer at the 10−21 level, Optics Express [27], 36886 (2019)
- Scientific Article: E. C. Cook et al., Resonant two-photon spectroscopy of the 2s3d 1D2 level of neutral 9Be Phys. Rev. Applied 101, 042503 (2020)
- Scientific Article: M. Collombon et al., Experimental Demonstration of Three-Photon Coherent Population Trapping in an Ion Cloud, Phys. Rev. Applied 12, 034035, (2019)
- Scientific Article: M. Collombon et al., Phase transfer between three visible lasers for coherent population trapping, Optics Letters Vol. 44, Issue 4 (2019)
- Scientific Article: A. Liehl et al., Ultrabroadband out-of-loop characterization of the carrier-envelope phase noise of an offset-free Er:fiber frequency comb. Optics Letters Vol. 42, Issue 10 (2017)
- Scientific Article: T. Puppe et al., Characterization of a DFG comb showing quadratic scaling of the phase noise with frequency, Optics Letters Vol. 41, Issue 8 (2016)
- Scientific Article: G. Krauss et al., All-passive phase locking of a compact Er:fiber laser system, Opt. Lett., 36, 540 (2011)
- Scientific Article: D. Fehrenbacher et al., Free-running performance and full control of a passively phase-stable Er:fiber frequency comb. Optica Vol. 2, Issue 10 (2015)
- Scientific Article: R. Kliese et al., Difference-frequency combs in cold atom physics, arXiv:1605.02426v1 (2016)
- Scientific Article: D. Brida et al., Ultrabroadband Er:fiber lasers, Laser & Photonics Review 8(3) (2014)
- Related Products